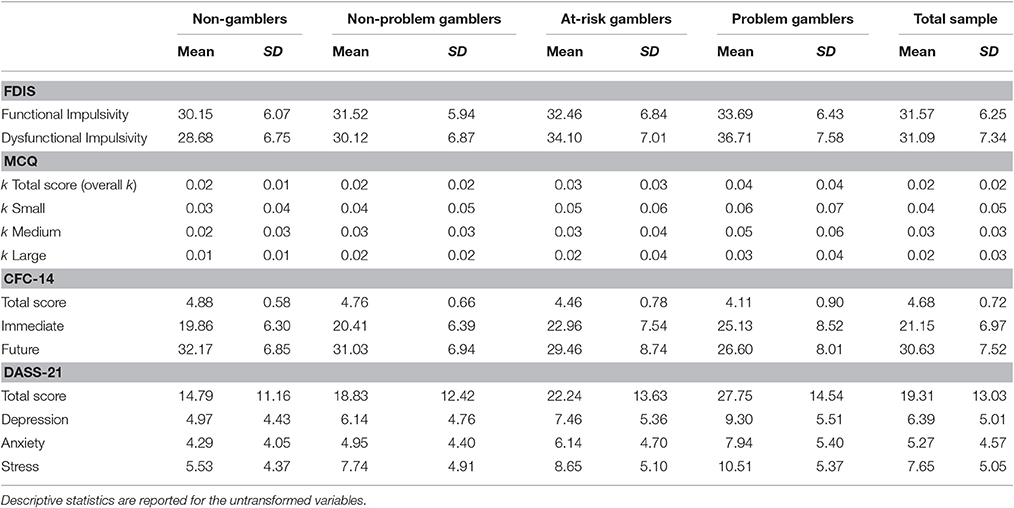
Sogs Gambling
The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS) is the only extensively used, validated screening tool for the evaluation of patients who are pathologic gamblers15.16 Although it is not validated, the.
| Availability | The instrument is freely available here: South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS) |
| Classification | |
| Short Description of Instrument | The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS) is a 20-item self-rated screening questionnaire based on DSM-III criteria for pathological gambling. The SOGS is the most commonly used instrument to screen for pathological or problem gambling in the general population. |
| Scoring | The SOGS has 20 items that are scored 0 or 1, with a total score of 1-4 suggesting problem gambling and a score =5 suggesting pathological gambling. |
| References | Lesieur HR, Blume SB. The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS): A new instrument for the identification of pathological gamblers. Am J Psychiatry 1987;144:1184–1188. |
- 614885 Rev 1/07/16 SOUTH OAKS GAMBLING SCREEN (SOGS) Assessment/Questionnaire Original: Medical Record Page 3 of 3. Created Date: 1/11/2016 8:08:50 AM.
- From folk and rock to country and hip-hop, there’s a gambling song in every genre. Check out our definitive top 31 list for the songs that really caught our attention through the decades.
Overview

Sogs Gambling Screen
The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS) is a screen used to measure pathological gambling. This 16-item instrument asks questions related to many gambling behaviours. It also asks questions about how the individual feels about his or her own gambling habits. SOGS classifies individuals into one of three categories: non-problem gambler, problem gambler and probable pathological gambling. The SOGS can be used by individuals as a self-assessment tool, and mental health practitioners can also use this tool to screen their clients. A modified version of the SOGS for adolescents is also available and includes 12 items.

Key Points
It is important to remember that this tool is not a diagnoses of pathological gambling, however, studies have shown the SOGS to be a reliable and valid measure of gambling problems. The items relate to the clinical symptoms of gambling problem as presented by the DSM. Some authors have raised concerns with some of the questions asked in the SOGS. Specifically, questions regarding the amount of debt that a gambler accumulates and questions about having a line of credit are considered poor, as they do not directly measure gambling problems.
References
Stinchfield, R. (2002). Reliability, validity, and classification accuracy of the South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS). Addictive Behaviors, 27(1), 1-19.
Songs Gambling Screen
Orford, J., Sproston, K., & Erens, B. (2003). SOGS and DSM-IV in the British Gambling Prevalence Survey: Reliability and factor structure. International Gambling Studies, 3(1), 53-65.
Sogs Gambling Screening
Young, M., & Stevens, M. (2008). SOGS and CGPI: Parallel comparison on a diverse population. Journal of Gambling Studies, 24(3), 337-356.